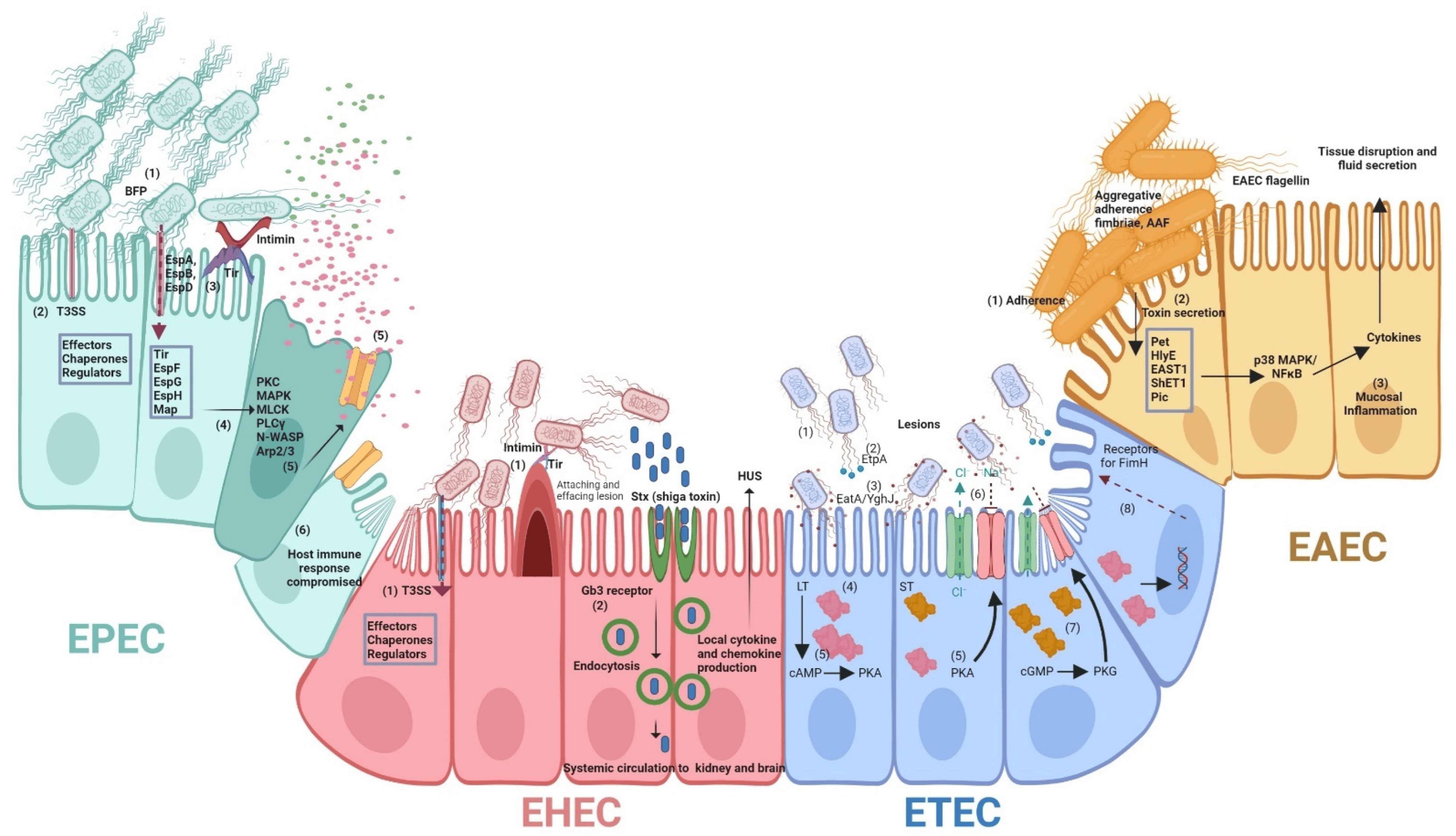
Escherichia coli O26 (E. coli O26) is a pathogenic strain of E. coli known for causing significant gastrointestinal illnesses. As part of the Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) group, E. coli O26 can lead to severe symptoms and potentially life-threatening complications. Effective testing and diagnostic measures are crucial for controlling infections and protecting public health. This article explores the role of testing in controlling E. coli O26 infections and highlights its importance in outbreak management and prevention strategies.
Understanding E. coli O26 Infections
- coli O26 infections typically present with a range of gastrointestinal symptoms, including severe abdominal cramps, diarrhea (often bloody), nausea, vomiting, and low-grade fever. In severe cases, infections can lead to hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), a condition characterized by hemolytic anemia, acute kidney failure, and thrombocytopenia. Young children, the elderly, and individuals with weakened immune systems are particularly vulnerable to severe outcomes.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of E. coli O26 infections is vital for several reasons:
- Timely Treatment: Early diagnosis allows for prompt medical intervention, which can help manage symptoms, prevent complications, and improve patient outcomes.
- Preventing Spread: Identifying infected individuals early can help prevent the spread of the bacteria to others, especially in communal settings such as schools, daycare centers, and nursing homes.
- Tracing the Source: Early detection aids in tracing the source of contamination, whether it’s a specific food product, water source, or environmental factor, enabling targeted control measures.
Diagnostic Methods for E. coli O26
Accurate diagnosis of E. coli O26 infections involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory testing. Key diagnostic methods include:
1. Stool Sample Analysis
Culture Testing: Stool samples are cultured to detect the presence of E. coli O26. Laboratories use selective media to isolate the bacteria and identify its specific strain. Culture testing is a standard method for diagnosing E. coli infections.
Shiga Toxin Testing: Since E. coli O26 produces Shiga toxins, stool samples can be tested for the presence of these toxins using enzyme immunoassays (EIA) or other toxin-detection methods.
2. Molecular Techniques
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR): PCR is a powerful molecular technique used to detect specific genetic markers associated with E. coli O26. PCR can rapidly identify the presence of E. coli O26 and its toxin-producing genes, providing accurate and timely results.
Whole-Genome Sequencing (WGS): WGS offers detailed genetic information about E. coli O26 strains. It can identify genetic variations, track the spread of infections, and provide insights into the bacteria’s virulence and resistance characteristics.
Surveillance and Outbreak Management
Testing plays a critical role in surveillance and outbreak management. Public health agencies, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA), rely on testing data to monitor trends, identify outbreaks, and implement control measures. Key aspects of surveillance and outbreak management include:
1. Routine Surveillance
- Monitoring Trends: Routine testing and surveillance programs help track the incidence of E. coli O26 infections over time. Monitoring trends can identify emerging threats and inform public health interventions.
- Outbreak Investigation
- Identifying Sources: In the event of an outbreak, testing helps identify the source of contamination, whether it’s a specific food product, water source, or environmental factor. Identifying the source is crucial for implementing targeted control measures and preventing further spread.
- Traceback Efforts: Traceback investigations involve tracing the contaminated product back to its origin, such as a specific farm, processing facility, or distribution center. Testing results play a vital role in guiding traceback efforts and pinpointing the source of contamination.
3. Public Health Responses
- Recalls and Advisories: When a contaminated product is identified, public health agencies may issue recalls and advisories to remove the product from the market and inform the public. Testing results provide the evidence needed to support these actions.
- Education and Outreach: Public health agencies use testing data to inform educational campaigns and outreach efforts. Educating the public about food safety practices, proper hygiene, and the risks associated with E. coli O26 can help prevent infections.
Conclusion
Testing plays a crucial role in controlling E. coli O26 infections by enabling early detection, guiding treatment, preventing spread, and supporting surveillance and outbreak management. Accurate and timely diagnostic methods, such as stool sample analysis, PCR, and WGS, are essential for identifying and managing infections. Public health agencies rely on testing data to monitor trends, investigate outbreaks, and implement control measures. By understanding the importance of testing and supporting robust testing programs, we can enhance our ability to prevent and control E. coli O26 infections and protect public health.